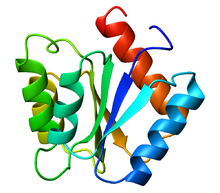
Flavodoxin
The structure of flavodoxin is characterized by a five-stranded parallel beta sheet, surrounded by five alpha helices.
These residues form a loop which may be used to increase the binding affinity of flavin mononucleotide as well as assist in the formation of folded intermediates.
Current research is being done to identify non toxic, Hp specific flavodoxin inhibitors for the purpose of treating infection.
This bond, as well as a common tryptophan residue near the binding site, aid in lowering SQ reactivity.
In cyanobacteria such as Nostoc sp., flavodoxins are heterocyst-specific,[10] and used in photosystem 1 to deliver electrons to nitrogenase, as well as reducing N2 and NADP+, nitrogen fixation and H2 formation.