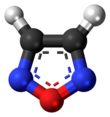
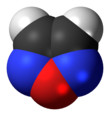
Furazan
Furazan, or 1,2,5-oxadiazole, is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound consisting of a five-atom ring containing 1 oxygen and 2 nitrogen atoms.
The formation of furazan from glyoxime is also exothermic and takes place with the copious evolution of noxious gases.
Furazan will evaporate at that temperature, which continuously removes the product from the reaction mixture.
The energetic precursor, diaminofurazan, can be prepared by heating diaminoglyoxime with potassium hydroxide followed by cooling to give white crystals.
Like many other furazans, diaminofurazan forms stable complexes with copper(II) salts.