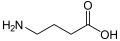
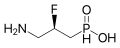
GABAB receptor
[3] GABABRs stimulate the opening of K+ channels, specifically GIRKs, which brings the neuron closer to the equilibrium potential of K+.
GABAB receptors also reduces the activity of adenylyl cyclase and Ca2+ channels by using G-proteins with Gi/G0 α subunits.
[4] GABAB receptors are involved in behavioral actions of ethanol,[5][6] gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB),[7] and possibly in pain.
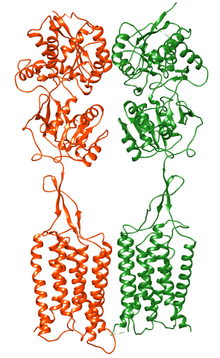
[10] There are two subunits of the receptor, GABAB1 and GABAB2,[11] and these appear to assemble as obligate heterodimers in neuronal membranes by linking up by their intracellular C termini.
[12] Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the full length GABAB receptor in different conformational states from inactive apo to fully active have been obtained.