Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase
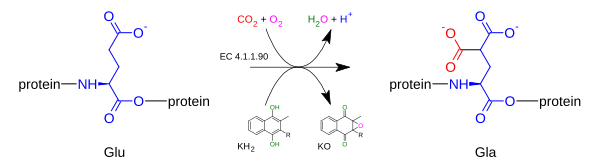
[4] Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the posttranslational modification of vitamin K-dependent proteins.
Many of these vitamin K-dependent proteins are involved in coagulation so the function of the encoded enzyme is essential for hemostasis.
Presence of two carboxylate groups causes chelation of Ca2+, resulting in change in tertiary structure of protein and its activation.
Based on the fact that the two reactions are coupled, a computational study is able to propose how the reactants interact with each other to form the products.
[5][12] This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.