Germ layer
Germ layers eventually give rise to all of an animal's tissues and organs through the process of organogenesis.
In 1817, Heinz Christian Pander discovered three primordial germ layers while studying chick embryos.
Diploblastic animals, Cnidaria and Ctenophora, show an increase in compartmentalization, having two germ layers, the endoderm and ectoderm.
All bilaterian animals (from flatworms to humans) are triploblastic, possessing a mesoderm in addition to the germ layers found in Diploblasts.
[5] In the human embryo, after about three days, the zygote forms a solid mass of cells by mitotic division, called a morula.
These transcription factors cause the pluripotent mouse embryonic stem cells to select a germ layer fate.
It also forms the lining cells of all the glands which open into the digestive tract, including those of the liver and pancreas; the epithelium of the auditory tube and tympanic cavity; the trachea, bronchi, and alveoli of the lungs; the bladder and part of the urethra; and the follicle lining of the thyroid gland and thymus.
The endoderm forms: the pharynx, the esophagus, the stomach, the small intestine, the colon, the liver, the pancreas, the bladder, the epithelial parts of the trachea and bronchi, the lungs, the thyroid, and the parathyroid.
Organs formed inside a coelom can freely move, grow, and develop independently of the body wall while fluid cushions protects them from shocks.
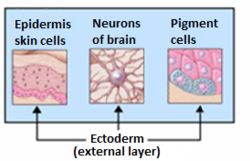
[14] The surface ectoderm develops into: epidermis, hair, nails, lens of the eye, sebaceous glands, cornea, tooth enamel, the epithelium of the mouth and nose.
The neural crest of the ectoderm develops into: peripheral nervous system, adrenal medulla, melanocytes, facial cartilage.
The neural tube of the ectoderm develops into: brain, spinal cord, posterior pituitary, motor neurons, retina.