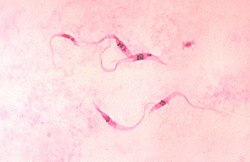
Giemsa stain
[citation needed] It stains the trophozoite Trichomonas vaginalis, which presents with greenish discharge and motile cells on wet prep.
It can be used for histopathological diagnosis of the Plasmodium species that cause malaria[2] and some other spirochete and protozoan blood parasites.
This is particularly relevant for detection of Cytomegalovirus infection, where the classical finding would be an "owl-eye" viral inclusion.
[4] Giemsa stains the fungus Histoplasma, Chlamydia bacteria, and can be used to identify mast cells.
[5] Giemsa's solution is a mixture of methylene blue, eosin, and Azure B.