Glutamate-sensitive fluorescent reporter
[2] In brain tissue, two-photon microscopy is typically used to monitor GluSnFR fluorescence.
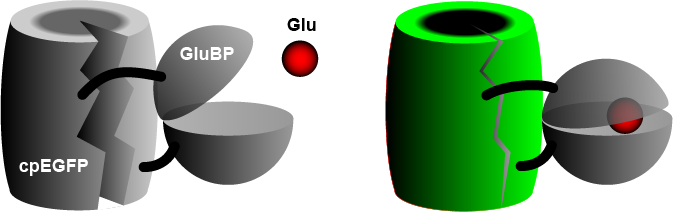
[3] When GluBP binds a glutamate molecule, it changes its shape, pulling the EGFP barrel together, increasing fluorescence.
A specific peptide segment (PDGFR) is included to bring the sensor to the outside of the cell membrane.
[4] In the more recent version by Aggarwal et al. (2022),[1] researchers introduced iGluSnFR to two additional anchoring domains, a glycosylphostidylinositol (GPI) anchor, and a modified form of the cytosolic -cterminal domain of Stargazin with a PDZ ligand.
[3] To measure synaptic transmission at high frequencies, novel iGluSnFR variants with accelerated kinetics have recently been developed.