GSK-3
[6] GS inhibition by GSK-3β leads to a decrease in glycogen synthesis in the liver and muscles, along with increased blood glucose or hyperglycemia.
Insulin indirectly inactivates GSK3 via downstream phosphorylation of the specific serine residues Ser21 and Ser9 in GSK-3 isoforms α and β, respectively via the PI3K/Akt pathway.
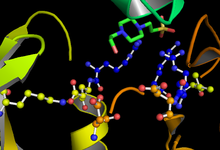
The active site, at residues 181, 200, 97, and 85, binds the terminal phosphate of ATP and transfers it to the target location on the substrate (see figure 1).
[16][17][18] GSK-3 is active in a number of central intracellular signaling pathways, including cellular proliferation, migration, glucose regulation, and apoptosis.
[2] After being primed by casein kinase 2 (CK2), glycogen synthase gets phosphorylated at a cluster of three C-terminal serine residues, reducing its activity.
GSK-3 participates in a number of signaling pathways in the innate immune response, including pro-inflammatory cytokine and interleukin production.
[22][23] The inactivation of GSK3B by various protein kinases also affects the adaptive immune response by inducing cytokine production and proliferation in naïve and memory CD4+ T cells.
[25] GSK-3 also participates in a number of apoptotic signaling pathways by phosphorylating transcription factors that regulate apoptosis.
[28] Overall, GSK-3 appears to both promote and inhibit apoptosis, and this regulation varies depending on the specific molecular and cellular context.
[25] Due to its importance across numerous cellular functions, GSK-3 activity is subject to tight regulation and is considered an "Ace" among kinases.
[22] Insulin indirectly inactivates GSK3 via downstream phosphorylation of the specific serine residues Ser21 and Ser9 in GSK-3 isoforms α and β, respectively, via the PI3K/Akt pathway (protein kinase B).
GSK-3 inhibitors are currently being tested for therapeutic effects in Alzheimer's disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), some forms of cancer, and bipolar disorder.
[35] GSK-3 activity has been associated with both pathological features of Alzheimer's disease, namely the buildup of amyloid-β (Aβ) deposits and the formation of neurofibrillary tangles.
GSK-3 is thought to directly promote Aβ production and to be tied to the process of the hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins, which leads to the tangles.
[28][38] GSK-3 also seems to be responsible for NFκB aberrant activity in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and pancreatic cancer cells.
[40] GSK-3 inhibitors increased in vivo CD8(+) OT-I CTL function and the clearance of viral infections by murine gamma-herpesvirus 68 and lymphocytic choriomeningitis clone 13 as well as anti-PD-1 in immunotherapy.
[41] In diabetes, GSK-3β inhibitors increase insulin sensitivity, glycogen synthesis, and glucose metabolism in skeletal muscles, and reduce obesity by affecting the adipogenesis process.
[49] Naproxen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug while cromolyn is an anti-allergic agent which acts as a mast cell stabilizer.
In vitro studies showed that famotidine inhibits GSK-3β activity and increases liver glycogen reserves in a dose dependent manner.
[53][54] Curcumin has wide pharmacological activities: anti-inflammatory,[55] anti-microbial,[56] hypoglycemic, anti-oxidant, and wound healing effects.
[57] In animal models with Alzheimer disease, it has anti-destructive effect of beta amyloid in the brain,[58] and recently it shows anti-malarial activity.
[59] Curcumin also has chemo preventative and anti-cancer effects,[citation needed] and it has been shown to attenuate oxidative stress and renal dysfunction in diabetic animals with chronic use.
[citation needed] NF-kB has two regulatory factors, IkB and GSK-3,[61] which suggests curcumin directly binds and inhibits GSK-3B.
[67] Some of them have been shown to fit the ATP-binding pocket of GSK-3β to lower blood glucose levels and improve some neuronal diseases.