Phenobarbital
[6] The IV or IM (injectable forms) may be used to treat status epilepticus if other drugs fail to achieve satisfactory results.
[20] The first-line drugs for treatment of status epilepticus are benzodiazepines, such as lorazepam, clonazepam, midazolam, or diazepam.
In massive doses, phenobarbital is prescribed to terminally ill people to allow them to end their life through physician-assisted suicide.
The electroencephalogram (EEG) of a person with phenobarbital overdose may show a marked decrease in electrical activity, to the point of mimicking brain death.
[40] Treatment of phenobarbital overdose is supportive, and mainly consists of the maintenance of airway patency (through endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation), correction of bradycardia and hypotension (with intravenous fluids and vasopressors, if necessary), and removal of as much drug as possible from the body.
In very large overdoses, multi-dose activated charcoal is a mainstay of treatment as the drug undergoes enterohepatic recirculation.
[41] Phenobarbital acts as an allosteric modulator which extends the amount of time the chloride ion channel is open by interacting with GABAA receptor subunits.
[42] Direct blockade of glutamatergic AMPA and kainate receptors are also believed to contribute to the hypnotic/anticonvulsant effect that is observed with phenobarbital.
It is one of the longest-acting barbiturates available – it remains in the body for a very long time (half-life of two to seven days) and has very low protein binding (20 to 45%).
Phenobarbital is metabolized by the liver, mainly through hydroxylation and glucuronidation and induces many isozymes of the cytochrome P450 system.
[45] The first barbiturate drug, barbital, was synthesized in 1902 by German chemists Emil Fischer and Joseph von Mering and was first marketed as Veronal by Friedr.
The young doctor Alfred Hauptmann[47] gave it to his epilepsy patients as a tranquilizer and discovered their seizures were susceptible to the drug.
Hauptmann dismissed concerns that its effectiveness in stalling seizures could lead to patients developing a build-up that needed to be "discharged".
The drug was quickly adopted as the first widely effective anti-convulsant, though World War I delayed its introduction in the U.S.[48] In 1939, a German family asked Adolf Hitler to have their disabled son killed; the five-month-old boy was given a lethal dose of Luminal after Hitler sent his own doctor to examine him.
A few days later 15 psychiatrists were summoned to Hitler's Chancellery and directed to commence a clandestine program of involuntary euthanasia.
[53][54] Phenobarbital was used to treat neonatal jaundice by increasing liver metabolism and thus lowering bilirubin levels.
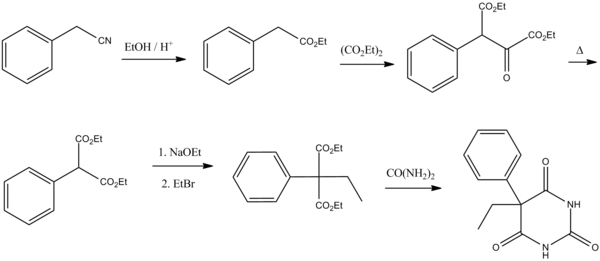
Barbiturate drugs are obtained via condensation reactions between a derivative of diethyl malonate and urea in the presence of a strong base.
The reason for this difference is because aryl halides do not typically undergo nucleophilic substitution in Malonic ester synthesis in the same way as aliphatic organosulfates or halocarbons do.
[36] The level of regulation includes Schedule IV non-narcotic (depressant) (ACSCN 2285) in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act 1970—but along with a few other barbiturates and at least one benzodiazepine, and codeine, dionine, or dihydrocodeine at low concentrations, it also has exempt prescription and had at least one exempt OTC combination drug now more tightly regulated for its ephedrine content.
[67] The phenobarbitone/phenobarbital exists in subtherapeutic doses which add up to an effective dose to counter the overstimulation and possible seizures from a deliberate overdose in ephedrine tablets for asthma, which are now regulated at the federal and state level as: a restricted OTC medicine and/or watched precursor, uncontrolled but watched/restricted prescription drug & watched precursor, a Schedule II, III, IV, or V prescription-only controlled substance & watched precursor, or a Schedule V (which also has possible regulations at the county/parish, town, city, or district as well aside from the fact that the pharmacist can also choose not to sell it, and photo ID and signing a register is required) exempt Non-Narcotic restricted/watched OTC medicine.
[69] British veterinarian Donald Sinclair, better known as the character Siegfried Farnon in the "All Creatures Great and Small" book series by James Herriot, committed suicide at the age of 84 by injecting himself with an overdose of phenobarbital.
Activist Abbie Hoffman also committed suicide by consuming phenobarbital, combined with alcohol, on 12 April 1989; the residue of around 150 pills was found in his body at autopsy.
[70] Thirty-nine members of the Heaven's Gate UFO cult committed mass suicide in March 1997 by drinking a lethal dose of phenobarbital and vodka "and then lay down to die" hoping to enter an alien spacecraft.