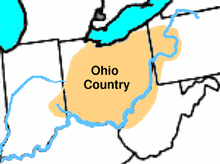
History of Ohio
Before that, Native Americans speaking Algonquin languages had inhabited Ohio and the central midwestern United States for hundreds of years, until displaced by the Iroquois in the latter part of the 17th century.
[citation needed] In Southern Ohio alone, archaeologists have pinpointed 10000 mounds used as burial sites and have excavated another 1000 earth-walled enclosures, including one enormous fortification with a circumference of about 3.5 miles, enclosing about 100 acres.
We now know from a great variety of items found in the mound tombs - large ceremonial blades chipped from obsidian rock formations in Yellowstone National Park; embossed breast-plates, ornaments and weapons fashioned from copper nuggets from the Great Lakes region; decorative objects cut from sheets of mica from the southern Appalachians; conch shells from the Atlantic seaboard; and ornaments made from shark and alligator teeth and shells from the Gulf of Mexico - that the Mound Builders participated in a vast trading network that linked together hundreds of Native Americans across the continent.
Sometime, presumably between the years 1100 and 1300 AD, Iroquoian people's began to aggressively expand their influence, conquering into Ohio from the northeast and displacing many of the preexisting cultures in the Great Lakes Region.
Overall, they managed to expand their territory through the North shore of Lakes Ontario and Erie, throughout Ohio, Indiana and southern Michigan and south from their original homeland in New York, all the way to the James River in Virginia when the war seems to have officially ended in 1701, but the French began aiding other native peoples who had fled west and took nearly all of that land for themselves, naming it the Illinois Colony.
During the war, the Sauk and Meskwaki tribes, who were Algonquian peoples displaced from the Ottawa River valley in Canada, migrated into Ohio and Michigan before the Iroquois quickly drove them all the way to Minnesota.
The Shawnee migrated from the southeast and were sometimes known as the Savannah, the Lenape had relocated from New Jersey and the Ottawa and Wyandot seem to have been formed from Algonquian, Huron and Anishinaabe captured by the Iroquois during the war, who broke free of their control.
[5] Squash and Pumpkins may be the oldest domesticated crop, having been grown by the Indian Knoll People of western Kentucky, who formed a complex society as far back as 8000 years ago.
With these more sophisticated weapons, the Five Nations nearly exterminated [citation needed] the Huron and all of the other Native Americans living immediately to their west in the Ohio country during the Beaver Wars, beginning in 1632.
Dunmore's War was fought between American colonists from Virginia and Shawnee roughly between Yellow Creek in Columbiana County and the modern-day West Virginia- Kentucky border.
Starting in the early 19th century, after the acquisition of the Louisiana Purchase, Congress began investing heavily in trying to convince Natives in the East to relocate west of the Mississippi.
The Royal Navy, in the midst of the Napoleonic Wars and constantly in need of manpower, had begun stopping American ships and impressing British deserters who had fled to the United States, angering the U.S. government and public and leading to a sharp deterioration in Anglo-American relations.
Manufacturers produced farming machinery, including Cincinnati residents Cyrus McCormick, who invented the reaper, and Obed Hussey, who developed an early version of the mower.
[63] Early on, the US was interested in creating a national public schooling system, but the irony came to be that, in Ohio, the various religious groups who had settled here refused to allow one another any say in what their own children would be taught, causing the issue to be constantly put on hold.
After public opinion in 1824 forced the state to find a resolution to the education problem, the legislature established the common school system in 1825 and financed it with a half-million property levy.
This was especially exasperated in the late 19th century, when racial violence against all sorts of people- including Native Americans- reached such a horrifying peak nationwide, that most such people went out of their ways to seem as white as possible.
Furthermore, women experienced a physical toll because they were expected to have babies, supervise the domestic chores, care for the sick, and take control of the garden crops and poultry.
Howard Chandler Christy, born in Morgan County, became a leading American artist during this century, as well as composer Dan Emmett, founder of the Blackface tradition.
[80] Immigration was cut off by the World War in 1914, allowing the ethnic communities to Americanize, grow much more prosperous, served in the military, and abandon possible plans to return to the old country.
Since then, there were larger influxes from the Jewish community, following World War II and a spike in the numbers of Middle Easterners following successive conflicts in the region during the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
The brothers gained the mechanical skills essential to their success by working for years in their Dayton, Ohio-based shop with printing presses, bicycles, motors, and other machinery.
Famous filmmakers include Steven Spielberg, Chris Columbus and the original Warner Brothers, who set up their first movie theatre in Youngstown, OH before that company later relocated to California.
The state produced many popular musicians, including Dean Martin, Doris Day, The O'Jays, Marilyn Manson, Dave Grohl of Nirvana and Foo Fighters fame, Devo, Macy Gray and The Isley Brothers.
Other famous individuals- native Ohioans and those who were just later associated with the state- include Annie Oakley, Clarence Darrow, Thomas Edison, Neil Armstrong and less beloved figures, like President William McKinley and General George Custer.
Ohio resident Harriet Beecher Stowe wrote the famous book Uncle Tom's Cabin, which was largely influential in shaping the opinion of the north against slavery.
Ohio-born Rutherford B. Hayes (1876), James A. Garfield (1880) and Benjamin Harrison (1888) were each nominated from a convention that had deadlocked, and where the delegates chose to turn to a candidate who could carry Ohio.
The key leaders included Samuel "Golden Rule" Jones in Toledo, Tom L. Johnson in Cleveland, Washington Gladden in Columbus, and James M. Cox in Cincinnati.
[123] Ohio was the scene of the Kent State Massacre, where four anti-Vietnam war protesters, although peaceful themselves, were shot dead, by badly frightened and poorly trained guardsmen.
Five Academy Award-winning films of the late 20th century were partly produced in the state, including The Deer Hunter, Rain Man, Silence of the Lambs, Terms of Endearment, and Traffic.
[136] It has been widely hailed as one of the nation's most successful government bureaucracies,[137] attracting 637 new high-tech companies to the state and 55,000 new jobs, with an average of salary of $65,000,[138] while having a $6.6 billion economic impact with an investment return ratio of 9:1.