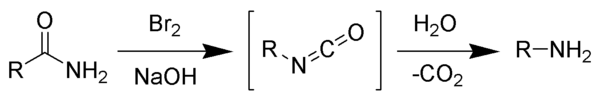
Hofmann rearrangement
The reaction can form a wide range of products, including alkyl and aryl amines.
The intermediate isocyanate is hydrolyzed to a primary amine, giving off carbon dioxide.
Sodium hypochlorite,[4] lead tetraacetate,[5] N-bromosuccinimide, and (bis(trifluoroacetoxy)iodo)benzene[6] can effect a Hofmann rearrangement.
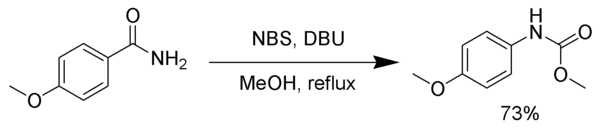
The intermediate isocyanate can be trapped with various nucleophiles to form stable carbamates or other products rather than undergoing decarboxylation.
[7] In a similar fashion, the intermediate isocyanate can be trapped by tert-butyl alcohol, yielding the tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc)-protected amine.