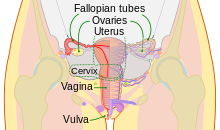
Female reproductive system
The female reproductive tract is made of several connected internal sex organs—the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes—and is prone to infections.
If no fertilization occurs, menstruation is the process by which the uterine lining is shed as blood, mucus, and tissue.
Semen containing spermatozoa is ejaculated from the penis at orgasm, into the vagina potentially enabling fertilization of the egg cell (ovum) to take place.
The cervix is the neck of the uterus, the lower, narrow portion where it joins with the upper part of the vagina.
In addition, contractions in the muscular wall of the uterus are important in pushing out the fetus at the time of birth.
Its major function is to accept a fertilized ovum, which becomes implanted into the endometrium, and derives nourishment from blood vessels, which develop exclusively for this purpose.
If the ovum is fertilized while in the fallopian tube, then it normally implants in the endometrium when it reaches the uterus, which signals the beginning of pregnancy.
In the absence of fertilization, the ovum will eventually traverse the entire reproductive tract from the fallopian tube until exiting the vagina through menstruation.
Oocytes residing in the primordial follicle of the ovary are in a non-growing prophase arrested state, but are capable of highly efficient homologous recombinational repair of DNA damages including double-strand breaks.
[11] It is difficult to determine any one organism most responsible for vaginitis because it varies from range of age, sexual activity, and method of microbial identification.
Vaginitis is not necessarily caused by a sexually transmitted infection as there are many infectious agents that make use of the close proximity to mucous membranes and secretions.
[12] This is a common cause of vaginal irritation and according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention at least 75% of adult women have experienced one at least once in their lifetime.
Other factors such as pregnancy, diabetes, weakened immune systems, tight fitting clothing, or douching can also be a cause.
Symptoms of yeast infections include itching, burning, irritation, and a white cottage-cheese-like discharge from the vagina.
Treatment varies from creams that can be applied in or around the vaginal area to oral tablets that stop the growth of fungus.
The most common two types of genital mutilation practiced are clitoridectomy, the circumcision of the clitoris and the excision of the clitoral prepuce.
They can all involve a range of adverse health consequences such as bleeding, irreparable tissue damage, and sepsis, which can sometimes prove fatal.
Genitoplasty refers to surgery that is carried out to repair damaged sex organs particularly following cancer and its treatment.
It is claimed in the Hippocratic writings that both males and females contribute their seed to conception; otherwise, children would not resemble either or both of their parents.
Four hundred years later, Galen identified the source of 'female semen' as the ovaries in female reproductive organs.

9. Vagina : 10. Hymen ; 11. Lumen; 12. Wall; 13. Fornix (lateral)
14. Uterus : Parts : 15. Cervix ; 16. Body and 17. Fundus . 18. Orifices: external and internal; 19. Cervical canal ; 20. Uterine cavity ; Layers : 21. Endometrium ; 22. Myometrium and 23. Perimetrium
24. Fallopian tube : 25. Isthmus ; 26. Ampulla ; 27. Infundibulum ; 28. Fimbriae (with 29. Fimbria ovarica)
30. Ovary
31. Visceral pelvic peritoneum : 32. Broad ligament (with 33. Mesosalpinx ; 34. Mesovarium and 35. Mesometrium )
Ligaments : 36. Round ; 37. Ovarian ; 38. Suspensory of ovary
Blood vessels : 39. Ovarian artery and vein ; 40. Uterine artery and veins ; 41. Vaginal artery and veins
Other : 42. Ureter ; 43. Pelvic floor ( Levator ani ); 44. Femoral head ; 45. Hip bone ; 46. Internal iliac vessels (anterior branches); 47. External iliac vessels ; 48. Abdominal cavity