Insulin (medication)
Repeated subcutaneous injection without site rotation can lead to lipohypertrophy and amyloidomas, which manifest as firm palpable nodules under the skin.
[16] Many obstacles associated with health behaviors also prevent people with type 2 diabetes mellitus from starting or intensifying their insulin treatment, including lack of motivation, lack of familiarity with or experience with treatments, and time restraints causing people to have high glycemic loads for extended periods of time prior to starting insulin therapy.
This is why managing the side effects associated with long-term early routine use of insulin for type 2 diabetes mellitus can prove to be a therapeutic and behavioral challenge.
Research on the Role of the Pancreas in Food Assimilation by Paulescu was published in August 1921 in the Archives Internationales de Physiologie, Liège, Belgium.
[28] Humulin was the first medication produced using modern genetic engineering techniques in which actual human DNA is inserted into a host cell (E. coli in this case).
These prevent the protein from spoiling or denaturing too rapidly, delay absorption of the insulin, adjust the pH of the solution to reduce reactions at the injection site, and so on.
However, a number of meta-analyses, including those done by the Cochrane Collaboration in 2005,[40] Germany's Institute for Quality and Cost Effectiveness in the Health Care Sector [IQWiG] released in 2007,[41] and the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technology in Health (CADTH)[42] also released in 2007 have shown no unequivocal advantages in clinical use of insulin analogues over more conventional insulin types.
Newer varieties are now pending regulatory approval in the US which are designed to work rapidly, but retain the same genetic structure as regular human insulin.
The limitations are cost, the potential for hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic episodes, catheter problems, and no "closed loop" means of controlling insulin delivery based on current blood glucose levels.
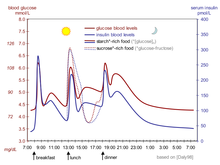
[56] Because of the complex and interacting factors, it is, in principle, impossible to know for certain how much insulin (and which type) is needed to 'cover' a particular meal to achieve a reasonable blood glucose level within an hour or two after eating.
For example, some people with diabetes require more insulin after drinking skim milk than they do after taking an equivalent amount of fat, protein, carbohydrate, and fluid in some other form.
One theoretical advantage of glargine and detemir is that they only need to be administered once a day, although in practice many people find that neither lasts a full 24 hours.
[62][63][64][65] Sliding scale insulin (SSI) is not an effective way of managing long-term diabetes in individuals residing in nursing homes.
With a prevalence of 6-20% among pregnant women globally, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as any degree of glucose intolerance developing or initially recognized during pregnancy.
The current perinatal guidelines recommend a low daily dose of insulin and take into account the woman's physiological features and the frequency of self-monitoring.
Close glucose monitoring is required to prevent hypoglycemia, which can potentially result in altered consciousness, seizures, and maternal damage.
[69] The possibility of using insulin in an attempt to improve athletic performance was suggested as early as the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Japan, as reported by Peter Sönksen in the July 2001 issue of Journal of Endocrinology.
Insulin-treated athletes are perceived to have lean body mass because physiological hyperinsulinemia in human skeletal muscle improves the activity of amino acid transport, which in turn promotes protein synthesis.
It decreases lipolysis and increases lipogenesis which is why bodybuilders and athletes use rhGH in conjunction with it as to offset this negative effect while maximizing protein synthesis.
Exogenous insulin injection creates an in-vivo hyperinsulinemic clamp, boosting muscle glycogen before and during the recovery phases of intense exercise.
Although a limited number of studies do suggest that insulin medication can be abused as a pharmacological treatment to boost strength and performance in young, healthy people or athletes, a recent assessment of the research argues that this is only applicable to a small group of "drug-naïve" individuals.
[78] The abuse of exogenous insulin carries with it an attendant risk of hypoglycemic coma and death when the amount used is in excess of that required to handle ingested carbohydrate.
Symptoms may include dizziness, weakness, trembling, palpitations, seizures, confusion, headache, drowsiness, coma, diaphoresis and nausea.
[82] Insulin is often measured in serum, plasma or blood in order to monitor therapy in people who are diabetic, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in hospitalized persons or assist in a medicolegal investigation of suspicious death.
[97] In 2019, it was estimated that people in the US pay two to six times more than the rest of the world for brand name prescription medicine, according to the International Federation of Health Plans.
"[98] Insulin, and all other medications, are supplied free of charge to people who use it to manage their diabetes by the National Health Services of the countries of the United Kingdom.
Accurate dosing was a particular problem, although people showed no significant weight gain or pulmonary function decline over the length of the trial when compared to the baseline.
[111] Following its commercial launch in 2005 in the United Kingdom, it was not (as of July 2006) recommended by National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence for routine use, except in cases where there is "proven injection phobia diagnosed by a psychiatrist or psychologist".
However, since serum antibody levels have been reported to increase without substantial clinical changes, acute bronchospasm in asthmatic and COPD patients along with a significant reduction in Diffusing Lung Capacity for Carbon Monoxide, in comparison to subcutaneous insulin, have been reported with its usage, Afrezza was given FDA approval with a warning (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy).
However, insulin is a peptide hormone, which is digested in the stomach and gut and in order to be effective at controlling blood sugar, cannot be taken orally in its current form.