Hyperpituitarism
In children with hyperpituitarism, disruption of growth regulation is rare, either because of hormone hypersecretion or because of manifestations caused by local compression of the adenoma.
[10] Cushing's disease diagnosis is done with a physical examination, laboratory tests and MRI of the pituitary gland (to locate tumors)[11] For prolactinoma, diagnosis comes in the form of the measurement of serum prolactin levels and MRI of pituitary gland.
[12] Treatment (for hyperpituitarism) in the case of prolactinoma consists of long-term medical management.
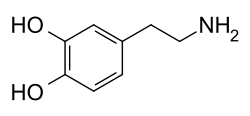
Dopamine agonists are strong suppressors of PRL secretion and establish normal gonadal function.
It also inhibits tumor cell replication (in some cases causes tumor shrinkage)[13] Treatment for gigantism begins with establishing target goals for IGF-1, transsphenoidal surgery (somatostatin receptor ligands- preoperatively) and postoperative imaging assessment.