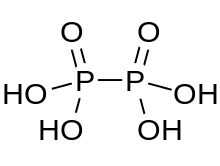
Hypophosphoric acid
In hypophosphoric acid the phosphorus atoms are identical and joined directly with a P−P bond.
Hypophosphoric acid can be prepared by the reaction of red phosphorus with sodium chlorite at room temperature.
[1] The disodium salt can be passed through an ion exchange column to form the acid dihydrate, H4P2O6·2H2O.
[2] The anhydrous acid can be formed by vacuum dehydration over P4O10 or by the reaction of H2S on lead hypophosphate, Pb2P2O6.
On standing in air, hypophosphates tend to oxidise to pyrophosphates containing the P2O4−7 ion where P has a formal oxidation state of +5.