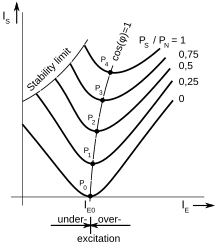
V curve
For a motor, points on the left of the minimum correspond to underexcitation (and therefore the armature current would "lag" the voltage), on the right - to overexcitation (and "lead").
Typically multiple V curves are plotted based on the experiments, each corresponding to its own load value.
also constant, any decrease in power factor has to be accommodated by a corresponding increase in the armature current
[3] While performing the correction, the motor can either provide the mechanical power also, or run in the idle mode ("float"), working as a synchronous condenser.
[5] The inverted V curve is a graph showing the relation of power factor as a function of field current.