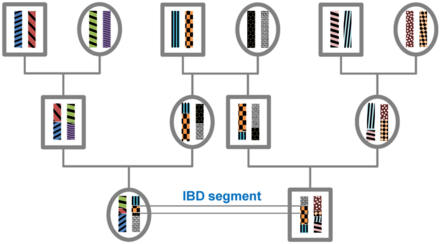
Identity by descent
[citation needed] All individuals in a finite population are related if traced back long enough and will, therefore, share segments of their genomes IBD.
The length of IBD segments that result from a common ancestor n generations in the past (therefore involving 2n meiosis) is exponentially distributed with mean 1/(2n) Morgans (M).
[6][14] Using simulated data, Browning and Thompson showed that IBD mapping has higher power than association testing when multiple rare variants within a gene contribute to disease susceptibility.
[11][15] Houwen et al. used IBD sharing to identify the chromosomal location of a gene responsible for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis in an isolated fishing population.
[16] Kenny et al. also used an isolated population to fine-map a signal found by a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of plasma plant sterol (PPS) levels, a surrogate measure of cholesterol absorption from the intestine.
[17] Francks et al. was able to identify a potential susceptibility locus for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder with genotype data of case-control samples.
[6][23][24][25][26] Gusev et al. showed that IBD segments can be used with additional modeling to estimate demographic history including bottlenecks and admixture.