Native Americans in the United States
"[25] After the thirteen British colonies revolted against Great Britain and established the United States, President George Washington and Secretary of War Henry Knox conceived the idea of "civilizing" Native Americans in preparation for their assimilation as U.S.
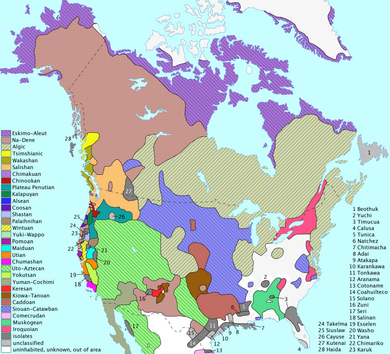
[citation needed] The history of Native Americans in the United States began before the founding of the U.S., tens of thousands of years ago with the settlement of the Americas by the Paleo-Indians.
The Eurasian migration to the Americas occurred over millennia via Beringia, a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska, as early humans spread southward and eastward, forming distinct cultures and societies.
By the 19th century, westward U.S. expansion, rationalized by Manifest destiny, pressured tribes into forced relocations like the Trail of Tears, which decimated communities and redefined Native territories.
A justification for the policy of conquest and subjugation of the Indigenous people emanated from the stereotyped perceptions of Native Americans as "merciless Indian savages" (as described in the United States Declaration of Independence).
By the 21st century, Native Americans had achieved increased control over tribal lands and resources, although many communities continue to grapple with the legacy of displacement and economic challenges.
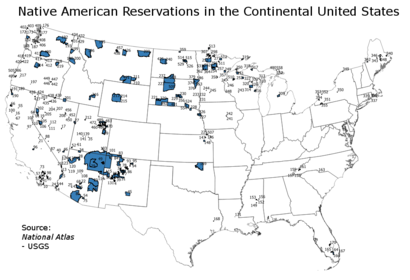
These tribes possess the right to form their own governments, to enforce laws (both civil and criminal) within their lands, to tax, to establish requirements for membership, to license and regulate activities, to zone, and to exclude persons from tribal territories.
Plecker pressured local governments into reclassifying all Native Americans in the state as "colored" and gave them lists of family surnames to examine for reclassification based on his interpretation of data and the law.
[91] The following is an excerpt from a statement from Mel Thom on May 1, 1968, during a meeting with Secretary of State Dean Rusk:[89] (It was written by members of the Workshop on American Indian Affairs and the NIYC) We have joined the Poor People's Campaign because most of our families, tribes, and communities number among those suffering most in this country.
This is largely due to the number of Native Americans having dwindled since white settler colonialism, while those who survived were forcibly moved into reservations; both of these factors were referenced by Adolf Hitler in 1928 when he admiringly stated the US had "gunned down the millions of Redskins to a few hundred thousand, and now keep the modest remnant under observation in a cage".
Among the most prominent of these were Elbridge Ayer Burbank, George Catlin, Seth Eastman, Paul Kane, W. Langdon Kihn, Charles Bird King, Joseph Henry Sharp, and John Mix Stanley.
These programs resembled the "sympathetic" yet contradictory film Dances With Wolves of 1990, in which, according to Ella Shohat and Robert Stam, the narrative choice was to relate the Lakota story as told through a Euro-American voice, for wider impact among a general audience.
Gilio-Whitaker, highlights some of the ways in which these practices are reinforced, with the concept of environmental deprivation – "historical processes of land and resource dispossession calculated to bring about the destruction of Indigenous lives and cultures."
“The consequences of capitalist economics, such as deforestation, water pollution, the clearing of land for large scale agriculture and urbanization, generate immediate disruptions on ecosystems "rapidly" rendering them very different from what they were like before, undermining Indigenous knowledge systems and Indigenous peoples' capacity to cultivate landscapes and adjust to environmental change.”[143] The Miami tribe, which now occupies Oklahoma, once resided in Oxford, Ohio, where Miami University now is placed.
After they were familiarized with their smallholder status, Native American landowners were lifted of trust restrictions and their land would get transferred back to them, contingent on a transactional fee to the federal government.
[178] Examples of historical trauma can be seen through the Wounded Knee Massacre of 1890, where over 200 unarmed Lakota were killed,[179] and the Dawes Allotment Act of 1887, when Native Americans lost four-fifths of their land.
For example, the re-introduction of the horse to North America allowed the Plains Indians to revolutionize their ways of life by making hunting, trading, and warfare far more effective, and to greatly improve their ability to transport possessions and move their settlements.
In the early years, as Native peoples encountered European explorers and settlers and engaged in trade, they exchanged food, crafts, and furs for blankets, iron and steel implements, horses, trinkets, firearms, and alcoholic beverages.
In the American Southwest, especially New Mexico, a syncretism between the Catholicism brought by Spanish missionaries and the native religion is common; the religious drums, chants, and dances of the Pueblo people are regularly part of Masses at Santa Fe's Saint Francis Cathedral.
Jim Thorpe, Lewis Tewanima, Joe Hipp, Notah Begay III, Chris Wondolowski, Jacoby Ellsbury, Joba Chamberlain, Kyle Lohse, Sam Bradford, Jack Brisco, Tommy Morrison, Billy Mills, Angel Goodrich, Shoni Schimmel, and Kyrie Irving are well known professional athletes.
With the win, he became just the fourth member of Team USA to capture the NBA championship and an Olympic gold medal in the same year, joining LeBron James, Michael Jordan, and Scottie Pippen.
Flutes and whistles made of wood, cane, or bone are also played, generally by individuals, but in former times also by large ensembles (as noted by Spanish conquistador de Soto).
In the International world of ballet dancing Maria Tallchief was considered America's first major prima ballerina,[224] and was the first person of Native American descent to hold the rank.
[233] Native artists such as Jeanne Rorex Bridges (Echota Cherokee) who was not enrolled ran the risk of fines or imprisonment if they continued to sell their art while affirming their Indian heritage.
For instance, Charles Eastman, a man of European and Lakota origin whose father sent both his sons to Dartmouth College, got his medical degree at Boston University and returned to the West to practice.
[248][249] In Colonial America, slavery soon became racialized, with those enslaved by the institution consisting of ethnic groups (non-Christian Native Americans and Africans) who were foreign to the Christian, European colonists.
Many surviving Native American peoples of the southeast strengthened their loose coalitions of language groups and joined confederacies such as the Choctaw, the Creek, and the Catawba for protection.
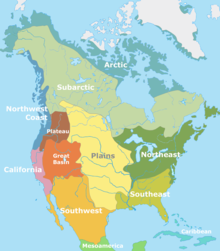
[265][266] As culture can vary widely between the 574 extant federally recognized tribes in the United States, the idea of a single unified "Native American" racial identity is a European construct that does not have an equivalent in tribal thought.
[271] Some tribes (particularly some in the Eastern United States) are primarily made up of individuals with an unambiguous Native American identity, despite having a large number of mixed-race citizens with prominent non-Native ancestry.
[301] The most popular theory is that human settlement of the Americas occurred in stages from the Bering sea coast line, with an initial 15,000 to 20,000-year layover on Beringia for the small founding population.