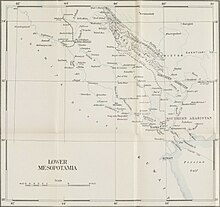
Lower Mesopotamia
It is located in the alluvial plain of Iraq from the Hamrin Mountains to the Faw Peninsula near the Persian Gulf.
[5] The medieval Arab geographers placed the northern border between Iraq and Upper Mesopotamia (the Jazirah) in a line running from Anbar on the Euphrates to Tikrit on the Tigris, although later it was shifted to a line running due west from Tikrit, thus including several towns on the Euphrates past Anbar into Iraq.
[6] An alluvial plain begins north of Tikrit Near Hamrin Mountains and extends to the Persian Gulf.
A fairly large area (15,000 km2 or 5,800 sq mi) just above the confluence of the two rivers at al Qurnah and extending east of the Tigris beyond the Iranian border is marshland, known as Lake Hammar, the result of centuries of flooding and inadequate drainage.
Because the waters of the Tigris and Euphrates above their confluence are heavily silt-laden, irrigation and fairly frequent flooding deposit large quantities of silty loam in much of the delta area.