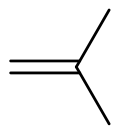
Isobutylene
It is a four-carbon branched alkene (olefin), one of the four isomers of butylene.
[3] Polymer and chemical grade isobutylene is typically obtained by dehydrating tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) or catalytic dehydrogenation of isobutane (Catofin or similar processes).
[4] Gasoline additives methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE), respectively, are produced by reacting methanol or ethanol with isobutylene contained in butene streams from olefin steam crackers or refineries, or with isobutylene from dehydrated TBA.
Polymerization of isobutylene produces butyl rubber (polyisobutylene or PIB).
tert-Butylamine is produced commercially by amination of isobutylene using zeolite catalysts:[6] Applications are found in the calibration of photoionization detectors.