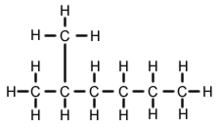
2-Methylhexane
It is structurally a hexane molecule with a methyl group attached to its second carbon atom.
Being an alkane, 2-methylhexane is insoluble in water, but is soluble in many organic solvents, such as alcohols and ether.
Within a group of isomers, those with more branches tend to ignite more easily and combust more completely.
At the presence of oxygen and flame, 2-methylhexane, like heptane, combusts mostly completely into water and carbon dioxide.
With UV-light and mixed with halogens in solvents, usually bromine in 1,1,1-trichloroethane, a substitution reaction occurs.