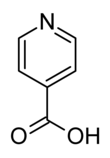
Isonicotinic acid
It is a derivative of pyridine with a carboxylic acid substituent at the 4-position.
On a commercial scale, isonicotinic acid, like other pyridine carboxylic acid is produced by ammoxidation of 4-picoline (4-methylpyridine) followed by hydrolysis of the resulting nitrile: It is also produced by oxidation of 4-picoline with nitric acid.
Hydrazide derivatives include isoniazid, iproniazid, and nialamide.
Amide and ester derivatives include ethionamide and dexamethasone isonicotinate.
Its conjugate base forms coordination polymers[3] and MOFs[4] by binding metal ions through both the N and carboxylate.