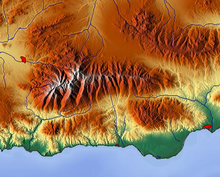
Terrain
The most common examples are used to derive slope or aspect of a terrain or curvatures at each location.
Climatic parameters are based on the modelling of solar radiation or air flow.
The most typical examples airlines of watersheds, stream patterns, ridges, break-lines, pools or borders of specific landforms.
A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid.
DEMs are used often in geographic information systems (GIS), and are the most common basis for digitally produced relief maps.