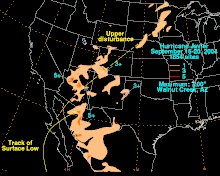
List of Arizona hurricanes
As a result, most storms that could affect Arizona are carried away from the United States, with only 6% of all Pacific hurricanes entering US territory.
These troughs tend to extend farther to the south during the latter part of the Pacific hurricane season, in the period between late August and early October.
In years when hurricanes approach Arizona, eastern and northern portions of the state receive on average 6–8% of the monsoon-season precipitation from tropical systems and their remnants.
[4] Tropical storms are one of Arizona's main sources of rainfall, as they infuse the monsoon over the southwestern United States with moisture, producing large-scale floods in occasions.
The last decade saw no storms reach Arizona while retaining tropical characteristics; however, numerous remnant lows caused heavy rainfall and flooding throughout the state.