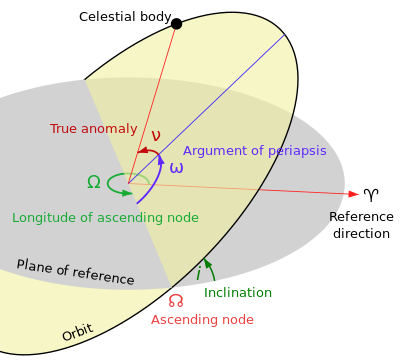
Longitude of the ascending node
[1] The ascending node is the point where the orbit of the object passes through the plane of reference, as seen in the adjacent image.
Commonly used reference planes and origins of longitude include: In the case of a binary star known only from visual observations, it is not possible to tell which node is ascending and which is descending.
In astrodynamics, the longitude of the ascending node can be calculated from the specific relative angular momentum vector h as follows: Here, n = ⟨nx, ny, nz⟩ is a vector pointing towards the ascending node.
The reference plane is assumed to be the xy-plane, and the origin of longitude is taken to be the positive x-axis.
For computation it is then, by convention, set equal to zero; that is, the ascending node is placed in the reference direction, which is equivalent to letting n point towards the positive x-axis.