List of orbits
This is a list of types of gravitational orbit classified by various characteristics.
[1] The following is a list of types of orbits: For orbits centered about planets other than Earth and Mars and for the dwarf planet Pluto, the orbit names incorporating Greek terminology are not as established and much less commonly used: For Earth orbiting satellites below the height of about 800 km, the atmospheric drag is the major orbit perturbing force out of all non-gravitational forces.
[11] Above 800 km, solar radiation pressure causes the largest orbital perturbations.
[12] However, the atmospheric drag strongly depends on the density of the upper atmosphere, which is related to the solar activity, therefore the height at which the impact of the atmospheric drag is similar to solar radiation pressure varies depending on the phase of the solar cycle.
Radial orbits can be either open or closed.
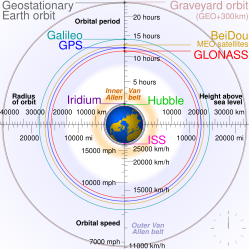


- the innermost, the red dotted line represents the orbit of the International Space Station (ISS);
- cyan represents low Earth orbit,
- yellow represents medium Earth orbit,
- The green dashed line represents the orbit of Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites, and
- the outermost, the black dashed line represents geostationary orbit.


