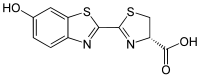
Luciferin
Luciferin (from Latin lucifer 'light-bearer') is a generic term for the light-emitting compound found in organisms that generate bioluminescence.
[1] Luciferins are a class of small-molecule substrates that react with oxygen in the presence of a luciferase (an enzyme) to release energy in the form of light.
[5] Bacterial luciferin is two-component system consisting of flavin mononucleotide and a fatty aldehyde found in bioluminescent bacteria.
[6] Coelenterazine is found in radiolarians, ctenophores, cnidarians, squid, brittle stars, copepods, chaetognaths, fish, and shrimp.
[10] This reaction and the luminescence produced is useful for imaging such as detecting tumors from cancer or capable of measuring gene expression.