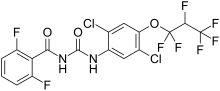
Lufenuron
Lufenuron is stored in the animal's body fat and transferred to adult fleas through the host's blood when they feed.
Adult fleas transfer it to their growing eggs through their blood, and to hatched larvae feeding on their excrement.
With its inner organs exposed to air, the insect dies from dehydration soon after hatching or molting (shedding its old, smaller shell).
[citation needed] Lufenuron is also used to fight fungal infections, since fungus cell walls are about one third chitin.
[1] Lufenuron is also sold as an agricultural pesticide for use against lepidopterans, eriophyid mites, and western flower thrips.