Mannitol salt agar
Mannitol salt agar or MSA is a commonly used selective and differential growth medium in microbiology.
[1] It contains a high concentration (about 7.5–10%) of salt (NaCl) which is inhibitory to most bacteria - making MSA selective against most Gram-negative and selective for some Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus, Enterococcus and Micrococcaceae) that tolerate high salt concentrations.
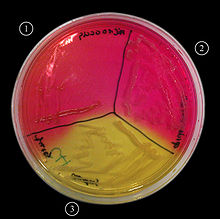
[2] It is also a differential medium for mannitol-fermenting staphylococci, containing the sugar alcohol mannitol and the indicator phenol red, a pH indicator for detecting acid produced by mannitol-fermenting staphylococci.
[3] Staphylococcus aureus produces yellow colonies with yellow zones, whereas other coagulase-negative staphylococci produce small pink or red colonies with no colour change to the medium.
[4] If an organism can ferment mannitol, an acidic byproduct is formed that causes the phenol red in the agar to turn yellow.