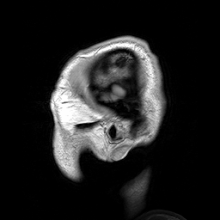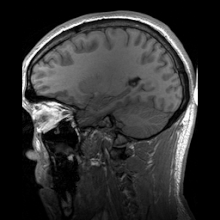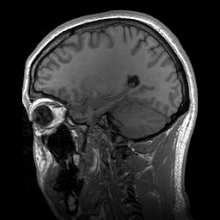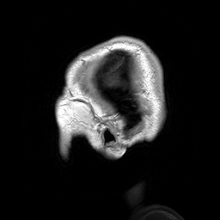
Medical physics
Medical physics of radiation therapy can involve work such as dosimetry, linac quality assurance, and brachytherapy.
The first type are mainly concerned with preparing students for a career as a hospital Medical Physicist and research focuses on improving the practice of the profession.
The scope often includes risks to workers and public particularly when these impact patient risk"The term "physical agents" refers to ionising and non-ionising electromagnetic radiations, static electric and magnetic fields, ultrasound, laser light and any other Physical Agent associated with medical e.g., x-rays in computerised tomography (CT), gamma rays/radionuclides in nuclear medicine, magnetic fields and radio-frequencies in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound in ultrasound imaging and Doppler measurements.
Material properties and applications studied in bionanoscience include mechanical properties (e.g. deformation, adhesion, failure), electrical/electronic (e.g. electromechanical stimulation, capacitors, energy storage/batteries), optical (e.g. absorption, luminescence, photochemistry), thermal (e.g. thermomutability, thermal management), biological (e.g. how cells interact with nanomaterials, molecular flaws/defects, biosensing, biological mechanisms such as mechanosensation), nanoscience of disease (e.g. genetic disease, cancer, organ/tissue failure), as well as computing (e.g. DNA computing) and agriculture (target delivery of pesticides, hormones and fertilizers.
Clinical (both "in-house" and "consulting") physicists[19] typically deal with areas of testing, optimization, and quality assurance of diagnostic radiology physics areas such as radiographic X-rays, fluoroscopy, mammography, angiography, and computed tomography, as well as non-ionizing radiation modalities such as ultrasound, and MRI.
[21][22][23] The academic and research side of therapeutic physics may encompass fields such as boron neutron capture therapy, sealed source radiotherapy, terahertz radiation, high-intensity focused ultrasound (including lithotripsy), optical radiation lasers, ultraviolet etc.
It is the science concerned with the recognition, evaluation, and control of health hazards to permit the safe use and application of ionizing radiation.
Health physics professionals promote excellence in the science and practice of radiation protection and safety.
Measurement methods include electrocardiography Many of these areas may be covered by other specialities, for example medical engineering or vascular science.