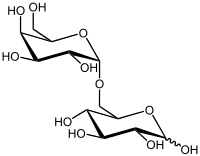
Melibiose
Melibiose is a reducing disaccharide formed by an α-1,6 linkage between galactose and glucose (D-Gal-(α1→6)-D-Glc).
[1][2] It differs from lactose in the chirality of the carbon where the galactose ring is closed and that the galactose is linked to a different point on the glucose moiety.
It can be formed by invertase-mediated hydrolysis of raffinose, which produces melibiose and fructose.
Melibiose can be broken down into its component saccharides, glucose and galactose, by the enzyme alpha-galactosidase, such as MEL1 from Saccharomyces pastorianus (lager yeast).
Melibiose cannot be used by Saccharomyces cerevisiae[3] (ale yeast), so this is one test to differentiate between the two yeast species.