MicroRNA sequencing
Evidence that dysregulated miRNAs play a role in diseases such as cancer[1] has positioned miRNA-seq to potentially become an important tool in the future for diagnostics and prognostics as costs continue to decrease.
[2] Like other miRNA profiling technologies, miRNA-Seq has both advantages (sequence-independence, coverage) and disadvantages (high cost, infrastructure requirements, run length, and potential artifacts).
[4][5][6] The first miRNA to be discovered, lin-4, was found in a genetic mutagenesis screen to identify molecular elements controlling post-embryonic development of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.
[7] The lin-4 gene encoded a 22 nucleotide RNA with conserved complementary binding sites in the 3’-untranslated region of the lin-14 mRNA transcript[8] and downregulated LIN-14 protein expression.
[9] miRNAs are now thought to be involved in the regulation of many developmental and biological processes, including haematopoiesis (miR-181 in Mus musculus[10]), lipid metabolism (miR-14 in Drosophila melanogaster[11]) and neuronal development (lsy-6 in Caenorhabditis elegans[12]).
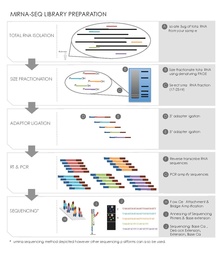
Sequencing preparation involved creating libraries by cloning of DNA reverse transcribed from endogenous small RNAs of 21–25 bp size selected by column and gel electrophoresis.
[17] Applied Biosystems SOLiD sequencing platform has also been used to examine the prognostic value of miRNAs in detecting human breast cancer.
[19][20] Reverse Transcription and PCR Amplification This step converts the small adaptor ligated RNAs into cDNA clones used in the sequencing reaction.
miRNAs may be preferentially expressed in certain cell types, tissues, stages of development, or in particular disease states such as cancer.
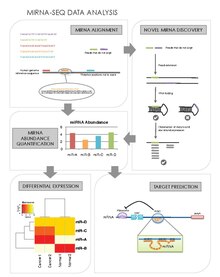
[21][26] Their general steps are as follows:[27] Another advantage of miRNA-seq is that it allows the discovery of novel miRNAs that may have eluded traditional screening and profiling methods.
[41][42] Validation of target cleavage in specific mRNAs is typically performed using a modified version of 5' Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends with a gene-specific primer.
In combination with the development of high-throughput profiling methods, miRNAs have been identified as biomarkers for cancer classification, response to therapy, and prognosis.
[48] Additionally, because miRNAs regulate gene expression they can also reveal perturbations in important regulatory networks that may be driving a particular disorder.