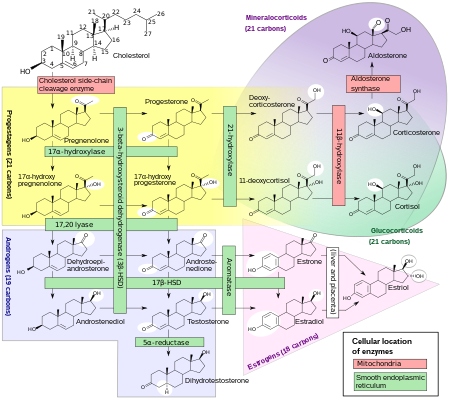
Mineralocorticoid
The name mineralocorticoid derives from early observations that these hormones were involved in the retention of sodium, a mineral.
Aldosterone is produced in the zona glomerulosa of the cortex of the adrenal gland and its secretion is mediated principally by angiotensin II but also by adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) and local potassium levels.
The hormone receptor without ligand binding interacts with heat shock proteins and prevents the transcription of targeted genes.
This enzyme, 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II (Protein:HSD11B2), catalyzes the deactivation of glucocorticoids to 11-dehydro metabolites.
The two main resulting problems: Hypoaldosteronism (the syndrome caused by underproduction of aldosterone) leads to the salt-wasting state associated with Addison's disease, although classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia and other disease states may also cause this situation.