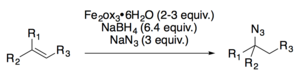Mukaiyama hydration
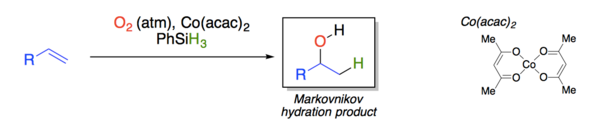
The Mukaiyama hydration is an organic reaction involving formal addition of an equivalent of water across an olefin by the action of catalytic bis(acetylacetonato)cobalt(II) complex, phenylsilane and atmospheric oxygen to produce an alcohol with Markovnikov selectivity.
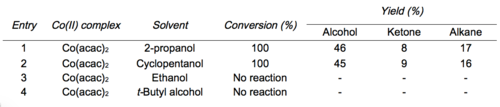
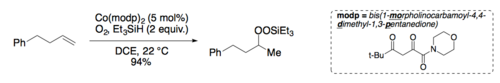
[3] Due to its chemoselectivity (tolerant of other functional groups) and mild reactions conditions (run under air at room temperature), the Mukaiyama hydration has become a valuable tool in chemical synthesis.
Homolysis generates a carbon centered radical that reacts directly with oxygen and is subsequently trapped by a cobalt(II) species to form the same cobalt-peroxide adduct as suggested by Mukaiyama.
[15] Dale Boger and coworkers used a variant of the Mukaiyama hydration, utilizing an iron oxalate catalyst (Fe2ox3•6H2O) in the presence of air, for the total synthesis of vinblastine and related analogs.
[17][18] Both Carreira[19] and Boger[20] have developed hydroazidation reactions.The Mukaiyama hydration or variants thereof have been featured in the syntheses of (±)-garsubellin A,[21] stigmalone,[22] vinblastine,[23] (±)-cortistatin A,[24] (±)-lahadinine B,[25] ouabagenin,[26] pectenotoxin-2,[27] (±)-indoxamycin B,[28] trichodermatide A,[29] (+)-omphadiol[30] and many more natural products.