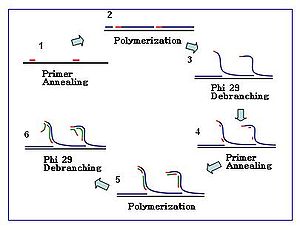
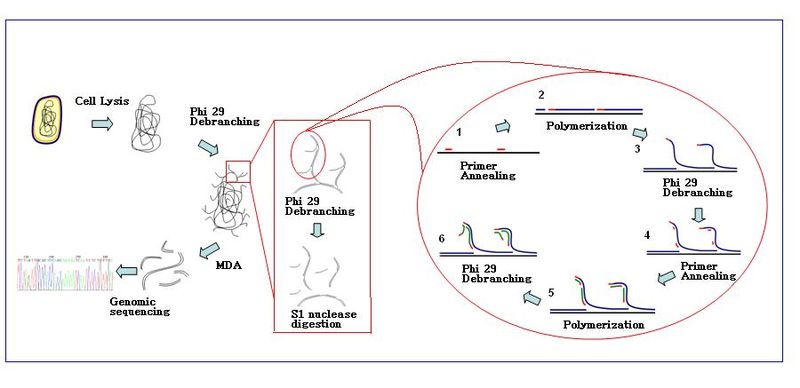
Multiple displacement amplification
Compared with conventional PCR amplification techniques, MDA does not employ sequence-specific primers but amplifies all DNA, generates larger-sized products with a lower error frequency, and works at a constant temperature.
The large fragment of Bst DNA polymerase is also used in MDA, but Ф29 is generally preferred due to its sufficient product yield and proofreading activity.
Further primer annealing and strand displacement on the newly synthesized template results in a hyper-branched DNA network.
[4] Products also have lower error rate and larger sizes compared to PCR based Taq amplification.
It is a powerful tool of amplifying DNA molecules from samples, such as uncultured microorganism or single cells to the amount that would be sufficient for sequencing studies.
It might affect the analysis of small stretches of genomic DNA in identifying Short Tandem Repeats (STR) alleles.
[19] Diseases with heterogeneous properties, such as cancer, also benefit from MDA-based genome sequencing's ability to study mutations in individual cells.
The MDA products from a single cell have also been successfully used in array-comparative genomic hybridization experiments, which usually require a relatively large amount of amplified DNA.
A method to circumvent this problem was proposed, which is based on conversion of these mixtures to circular concatemers using ligation, followed by Φ29 DNA polymerase-mediated MDA.
[20] The trace amount of samples collected from crime scenes can be amplified by MDA to the quantity that is enough for forensic DNA analysis, which is commonly used in identifying victims and suspects.