Nehalem (microarchitecture)
Nehalem /nəˈheɪləm/[1] is the codename for Intel's 45 nm microarchitecture released in November 2008.
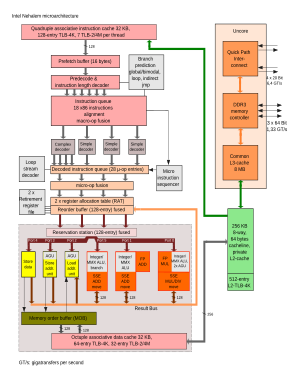
[4][5] Nehalem is built on the 45 nm process, is able to run at higher clock speeds without sacrificing efficiency, and is more energy-efficient than Penryn microprocessors.
Nehalem is an architecture that differs radically from NetBurst, while retaining some of the latter's minor features.
Nehalem later received a die-shrink to 32 nm with Westmere, and was fully succeeded by "second-generation" Sandy Bridge in January 2011.
[13] Compared to Penryn, Nehalem has: Overclocking is possible with Bloomfield processors and the X58 chipset.