New South Wales
In 1770, James Cook charted the unmapped eastern coast of the continent of New Holland, now Australia, and claimed the entire coastline that he had just explored as British territory.
[12][a] In January 1788 Arthur Phillip arrived in Botany Bay with the First Fleet of 11 vessels, which carried over a thousand settlers, including 736 convicts.
However, after the departure of Governor Phillip, the colony's military officers began acquiring land and importing consumer goods obtained from visiting ships.
[20] Poorly armed, and with their leader Philip Cunningham captured, about 100 troops and volunteers routed the main body of insurgents at Rouse Hill.
[23] A road across the Blue Mountains was completed in 1815, opening the way for large scale farming and grazing in the lightly wooded pastures west of the Great Dividing Range.
[25] New South Wales established a military outpost on King George Sound in Western Australia in 1826 which was later transferred to the Swan River colony.
In 1836, an annual licence was introduced in an attempt to control the pastoral industry, but booming wool prices and the high cost of land in the settled areas encouraged further squatting.
The expansion of the pastoral industry led to violent episodes of conflict between settlers and traditional Aboriginal landowners, such as the Myall Creek massacre of 1838.
[33] The transportation of convicts to New South Wales ended in 1840, and in 1842 a Legislative Council was introduced, with two-thirds of its members elected and one-third appointed by the governor.
Parkes also struck a deal with Edmund Barton, leader of the NSW Protectionist Party, whereby they would work together for federation and leave the question of a protective tariff for a future Australian government to decide.
[47][48] The outbreak of the First World War in 1914 saw more NSW volunteers for service than the federal authorities could handle, leading to unrest in camps as recruits waited for transfer overseas.
Despite a huge victory for Holman's pro-conscription Nationalists in the elections of March 1917, a second referendum on conscription held in December that year was defeated in New South Wales and nationally.
[49] Following the war, NSW governments embarked on large public works programs including road building, the extension and electrification of the rail network and the construction of the Sydney Harbour Bridge.
In 1931 Lang proposed a plan to deal with the depression which included a suspension of interest payments to British creditors, diverting the money to unemployment relief.
The NSW Lang government subsequently defaulted on overseas interest payments and was dismissed from office in May 1932 by the governor, Sir Phillip Game.
The post-war economic boom brought near-full employment and rising living standards, and the government engaged in large spending programs on housing, dams, electricity generation and other infrastructure.
His replacement Barrie Unsworth struggled to emerge from Wran's shadow and lost a 1988 election against a resurgent Liberal Party led by Nick Greiner.
Tourism is important to the economies of coastal towns such as Coffs Harbour, Lismore, Nowra and Port Macquarie, but the region also produces seafood, beef, dairy, fruit, sugar cane and timber.
[citation needed] There are numerous forests in New South Wales, with such tree species as Red Gum Eucalyptus and Crow Ash (Flindersia australis), being represented.
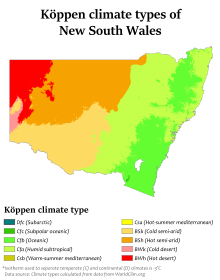
[76] The climate along the flat, coastal plain east of the range varies from oceanic in the south to humid subtropical in the northern half of the state, right above Wollongong.
The Northern Tablelands, which are also on the North coast, have relatively mild summers and cold winters, due to their high elevation on the Great Dividing Range.
[note 8][86] According to the 2021 census, 29.5% of people in New South Wales speak a language other than English at home with Mandarin (3.4%), Arabic (2.8%), Cantonese (1.8%), Vietnamese (1.5%) and Hindi (1.0%) being the most popular.
In 2006, the Constitution Amendment Pledge of Loyalty Act 2006 No 6,[92] was enacted to amend the NSW Constitution Act 1902 to require Members of the New South Wales Parliament and its Ministers to take a pledge of loyalty to Australia and to the people of New South Wales instead of swearing allegiance to Elizabeth II her heirs and successors, and to revise the oaths taken by Executive Councillors.
[129] These parks range from rainforests, waterfalls, rugged bush to marine wonderlands and outback deserts, including World Heritage sites.
[132] This government agency is responsible for developing and maintaining the parks and reserve system, and conserving natural and cultural heritage, in the state of New South Wales.
The Stadium Australia hosts major events including the NRL Grand Final, State of Origin, rugby union and soccer internationals.
Other professional teams include: As Australia's most populous state, New South Wales is home to a number of cultural institutions of importance to the nation.
[citation needed] New South Wales is the setting and shooting location of many Australian films, including Mad Max 2, which was shot near the mining town of Broken Hill.
The state has also attracted international productions, both as a setting, such as in Mission: Impossible 2, and as a stand-in for other locations, as seen in The Matrix franchise, The Great Gatsby and Unbroken.
[138] New South Wales in recent history has pursued bilateral partnerships with other federated states/provinces and metropolises through establishing a network of sister state relationships.