Non-renewable resource
It is projected that fossil-based resources will eventually become too costly to harvest and humanity will need to shift its reliance to renewable energy such as solar or wind power.
Since the dawn of internal combustion engine technologies in the 19th century, petroleum and other fossil fuels have remained in continual demand.
As a result, conventional infrastructure and transport systems, which are fitted to combustion engines, remain predominant around the globe.
The modern-day fossil fuel economy is widely criticized for its lack of renewability, as well as being a contributor to climate change.
[7] The American Petroleum Institute likewise does not consider conventional nuclear fission as renewable, but rather that breeder reactor nuclear power fuel is considered renewable and sustainable, noting that radioactive waste from used spent fuel rods remains radioactive and so has to be very carefully stored for several hundred years.
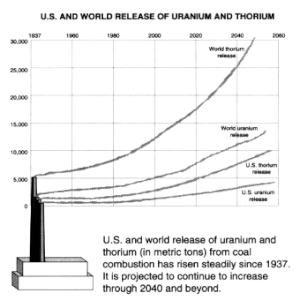
[9] The use of nuclear technology relying on fission requires naturally occurring radioactive material as fuel.
Uranium, the most common fission fuel, is present in the ground at relatively low concentrations and mined in 19 countries.
[12] In 2014, with the advances made in the efficiency of seawater uranium extraction, a paper in the journal of Marine Science & Engineering suggests that with, light water reactors as its target, the process would be economically competitive if implemented on a large scale.
[14] Nuclear energy production is associated with potentially dangerous radioactive contamination as it relies upon unstable elements.
[17] The storage of this unused uranium and the accompanying fission reaction products has raised public concerns about risks of leaks and containment, however studies conducted on the natural nuclear fission reactor in Oklo Gabon, have informed geologists on the proven processes that kept the waste from this 2 billion year old natural nuclear reactor.
In the natural environment water, forests, plants and animals are all renewable resources, as long as they are adequately monitored, protected and conserved.
The overfishing of the oceans is one example of where an industry practice or method can threaten an ecosystem, endanger species and possibly even determine whether or not a fishery is sustainable for use by humans.
[28] The Hartwick's rule provides an important result about the sustainability of welfare in an economy that uses non-renewable resources.