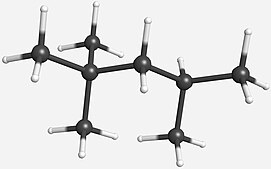
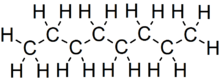Octane
Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the location of branching in the carbon chain.
One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane), is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.
Under standard temperature and pressure, octane is an odorless, colorless liquid.
Like other short-chained alkanes with a low molecular weight, it is volatile, flammable, and toxic.
[6] A common route to such fractions is the alkylation reaction between iso-butane and 1-butene, which forms iso-octane.