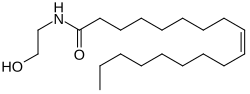
Oleoylethanolamide
Oleoylethanolamide (OEA) is an endogenous peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α) agonist.
It is a naturally occurring ethanolamide lipid that regulates feeding and body weight in vertebrates ranging from mice to pythons.
[5] This produces an N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine, which is then split (hydrolyzed) by N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) into phosphatidic acid and OEA.
[9] OEA has been reported to lengthen the life span of the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans through interactions with lysomal molecules.
In this sense, recent research has demonstrated that OEA reduces neuronal death in a murine model of aggressive neurodegeneration.