Oppenauer oxidation
The Oppenauer oxidation is commonly used in various industrial processes such as the synthesis of steroids, hormones, alkaloids, terpenes, etc.
The aluminium-catalyzed hydride shift from the α-carbon of the alcohol to the carbonyl carbon of acetone proceeds over a six-membered transition state (8).
Reaction conditions are mild and gentle since the substrates are generally heated in acetone/benzene mixtures.
For example, Woodward used potassium tert-butoxide and benzophenone for the oxidation of quinine to quininone, as the traditional aluminium catalytic system failed to oxidize quinine due to the complex formed by coordination of the Lewis-basic nitrogen to the aluminium centre.
For example, a highly active aluminium catalyst was reported by Maruoka and co-workers which was utilized in the oxidation of carveol to carvone (a member of a family of chemicals called terpenoids) in excellent yield (94%).
The Oppenauer oxidation is used to prepare analgesics in the pharmaceutical industry such as morphine and codeine.
[4] Another general side reaction is the migration of the double bond during the oxidation of allylic alcohol substrates.






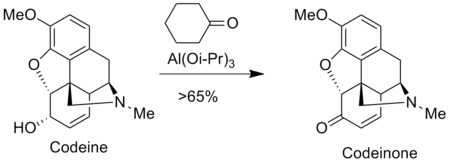




![Oppenauer oxidation of a steroid derivative.[15]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/36/Wiki-oppenaure-mxa2.tif/lossy-page1-350px-Wiki-oppenaure-mxa2.tif.jpg)