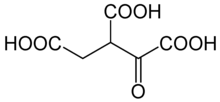
Oxalosuccinic acid
Oxalosuccinic acid/oxalosuccinate is an unstable 6-carbon intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
It's a keto acid, formed during the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to alpha-ketoglutarate, which is catalyzed by the enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase.
Isocitrate is first oxidized by coenzyme NAD+ to form oxalosuccinic acid/oxalosuccinate.
[1] Oxalosuccinic acid is both an alpha-keto and a beta-keto acid (an unstable compound) and it is the beta-ketoic property that allows the loss of carbon dioxide in the enzymatic reaction in conversion to the five-carbon molecule 2-oxoglutarate.
[2] Acetyl-CoAOxaloacetateMalateFumarateSuccinateSuccinyl-CoACitratecis-AconitateIsocitrateOxalosuccinate2-oxoglutarateThis biochemistry article is a stub.