Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
PI3Ks are a family of related intracellular signal transducer enzymes capable of phosphorylating the 3 position hydroxyl group of the inositol ring of phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns).
[3][4] The discovery of PI3Ks by Lewis Cantley and colleagues began with their identification of a previously unknown phosphoinositide kinase associated with the polyoma middle T protein.
[9] Class I PI3Ks are heterodimeric molecules composed of a regulatory and a catalytic subunit; they are further divided between IA and IB subsets on sequence similarity.
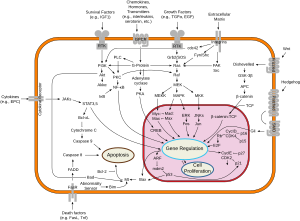
PI3Ks have been linked to an extraordinarily diverse group of cellular functions, including cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking.
Many of these functions relate to the ability of class I PI3Ks to activate protein kinase B (PKB, aka Akt) as in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Full activation of AKT occurs upon phosphorylation of serine 473 by the TORC2 complex of the mTOR protein kinase.
[19] Many other proteins have been identified that are regulated by PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, including Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), General Receptor for Phosphoinositides-1 (GRP1), and the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase.
In addition, the epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR that functions upstream of PI3K is mutationally activated or overexpressed in cancer.
In mouse hippocampal CA1 neurons, certain PI3Ks are complexed with AMPA receptors and compartmentalized at the postsynaptic density of glutamatergic synapses.
[24] PI3Ks are phosphorylated upon NMDA receptor-dependent CaMKII activity,[25] and it then facilitates the insertion of AMPA-R GluR1 subunits into the plasma membrane.
[29] The PI3K-mTOR pathway leads to the phosphorylation of p70S6K, a kinase that facilitates translational activity,[31][32] further suggesting that PI3Ks are required for the protein-synthesis phase of LTP induction instead.
PI3Ks interact with the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) to regulate glucose uptake through a series of phosphorylation events.
[citation needed] All PI3Ks are inhibited by the drugs wortmannin and LY294002, although certain members of the class II PI3K family show decreased sensitivity.
Co-targeted inhibition of the pathway with other pathways such as MAPK or PIM has been highlighted as a promising anti-cancer therapeutic strategy, which could offer benefit over the monotherapeutic approach by circumventing compensatory signalling, slowing the development of resistance and potentially allowing reduction of dosing.