Pain
[7] Psychological factors such as social support, cognitive behavioral therapy, excitement, or distraction can affect pain's intensity or unpleasantness.
Vigorous vibration or electrical stimulation of the stump, or current from electrodes surgically implanted onto the spinal cord, all produce relief in some patients.
[23]: 61–69 Mirror box therapy produces the illusion of movement and touch in a phantom limb which in turn may cause a reduction in pain.
Episodic analgesia may occur under special circumstances, such as in the excitement of sport or war: a soldier on the battlefield may feel no pain for many hours from a traumatic amputation or other severe injury.
[38] If I have matters right, the consequences of pain will include direct physical distress, unemployment, financial difficulties, marital disharmony, and difficulties in concentration and attention…Although pain is considered to be aversive and unpleasant and is therefore usually avoided, a meta-analysis which summarized and evaluated numerous studies from various psychological disciplines, found a reduction in negative affect.
Across studies, participants that were subjected to acute physical pain in the laboratory subsequently reported feeling better than those in non-painful control conditions, a finding which was also reflected in physiological parameters.
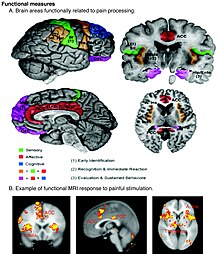
There were several competing early theories of pain among the ancient Greeks: Hippocrates believed that it was due to an imbalance in vital fluids.
However, after a series of clinical observations by Henry Head and experiments by Max von Frey, the psychologists migrated to specificity almost en masse.
At the peripheral end of the nociceptor, noxious stimuli generate currents that, above a given threshold, send signals along the nerve fiber to the spinal cord.
The "specificity" (whether it responds to thermal, chemical, or mechanical features of its environment) of a nociceptor is determined by which ion channels it expresses at its peripheral end.
Some of the paleospinothalamic fibers peel off in the brain stem—connecting with the reticular formation or midbrain periaqueductal gray—and the remainder terminate in the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus.
[52] The authors proposed that the thin C and A-delta (pain) and large diameter A-beta (touch, pressure, vibration) nerve fibers carry information from the site of injury to two destinations in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, and that A-beta fiber signals acting on inhibitory cells in the dorsal horn can reduce the intensity of pain signals sent to the brain.
[53] (p. 432) The paper ends with a call to action: "Pain can be treated not only by trying to cut down the sensory input by anesthetic block, surgical intervention and the like, but also by influencing the motivational-affective and cognitive factors as well.
[58] In pain science, thresholds are measured by gradually increasing the intensity of a stimulus in a procedure called quantitative sensory testing which involves such stimuli as electric current, thermal (heat or cold), mechanical (pressure, touch, vibration), ischemic, or chemical stimuli applied to the subject to evoke a response.
A change in condition that deviates from baseline, such as moaning with movement or when manipulating a body part, and limited range of motion are also potential pain indicators.
In patients who possess language but are incapable of expressing themselves effectively, such as those with dementia, an increase in confusion or display of aggressive behaviors or agitation may signal that discomfort exists, and further assessment is necessary.
[73] This has been postulated to lead to extended emergency room wait times for women and frequent dismissal of their ability to accurately report pain.
[29] People with long-term pain frequently display psychological disturbance, with elevated scores on the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory scales of hysteria, depression and hypochondriasis (the "neurotic triad").
[94][95] In the US, African and Hispanic Americans are more likely than others to suffer unnecessarily while in the care of a physician;[96][97] and women's pain is more likely to be undertreated than men's.
[101] In 2011, Human Rights Watch alerted that tens of millions of people worldwide are still denied access to inexpensive medications for severe pain.
Sugar (sucrose) when taken by mouth reduces pain in newborn babies undergoing some medical procedures (a lancing of the heel, venipuncture, and intramuscular injections).
[110] Sweet liquid by mouth moderately reduces the rate and duration of crying caused by immunization injection in children between one and twelve months of age.
[119] Spinal manipulation produces the same outcome as other treatments, such as general practitioner care, pain-relief drugs, physical therapy, and exercise, for acute (short-term) lower back pain.
[127] In various contexts, the deliberate infliction of pain in the form of corporal punishment is used as retribution for an offence, for the purpose of disciplining or reforming a wrongdoer, or to deter attitudes or behaviour deemed unacceptable.
In Western societies, the intentional infliction of severe pain (torture) was principally used to extract confession prior to its abolition in the latter part of the 19th century.
Torture as a means to punish the citizen has been reserved for offences posing a severe threat to the social fabric (for example, treason).
[128] The administration of torture on bodies othered by the cultural narrative, those observed as not 'full members of society' [128]: 101–121[AD1] met a resurgence in the 20th century, possibly due to the heightened warfare.
[129] The use of pain to transition to a 'cleansed and purified' state is seen in religious self-flagellation practices (particularly those of Christianity and Islam), or personal catharsis in neo-primitive body suspension experiences.
[137][140][141] The presence of pain in animals is unknown, but can be inferred through physical and behavioral reactions,[142] such as paw withdrawal from various noxious mechanical stimuli in rodents.
[144] Nevertheless, no member of the plant kingdom does feel pain notwithstanding their abilities to respond to sunlight, gravity, wind, and any external stimuli such as insect bites since they lack any nervous system.