Tactile hallucination
[1] Weber distinctly identified these two types of sensation as the sense of touch and common bodily sensibility.
Ramachandran have analyzed and attributed tactile hallucinations as a dysfunctional perception of the brain as opposed to just a symptom related to insanity.
[3] The most common tactile hallucination in patients with schizophrenia is a sensation in which a patch of their skin is stretched elastically across their head.
[4] Patients with schizophrenia also have a hard time portraying emotions as they divert most of their energy to control the pain from their tactile hallucinations.
[6] These hallucinations were aggravated during evening times due to altered arousal states and were alleviated by dopaminergic treatment such as the intake of clozapine.
[9][10] Tactile hallucinations in RLS include feelings of itching, pulling, crawling or creeping mainly in the legs, with the accompanying overwhelming urge to move them.
[9] The causes of RLS are generally unknown, though there are three major hypotheses: iron deficiency, dopamine insufficiency and genetic inheritance.
[9] Treatments for RLS typically focus on symptom relief through supplementing iron, blocking nerve receptors through the use of alpha-2 delta drugs such as gabapentin, or through the use of opioids or benzodiazepines.
[11] Patients that experience this phantom limb pain are very important in research studies for their role in determining brain plasticity.
The vivid tactile sensation of the arm that is no longer present suggest the highly complex nature of the brain to reorganize different functions which were once thought to be hardwired to specific regions (localization).
Cocaine and alcohol can induce rapid firing of neuronal cells of the somatosensory region of the brain leading to vivid perception of illusionary bugs on the skin.
[1] Cenesthopathic hallucinatory experiences are caused by the hyperactive neuronal stimulation of the primary somatosensory cortex due to a disorder or a damage to this area.
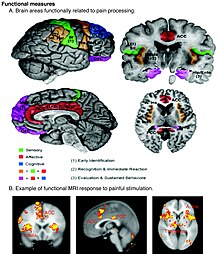
[2] Tactile sensory input is produced and conducted through the spinal cord and thalamus and it is received at the primary somatosensory cortex.
Once it has reached the primary somatosensory cortex, it is distributed across the brain and it will not be processed unless it is important and one pays close attention to the information based on a specific context.
Even with complete sensory deprivation, discrete tactile memories can trigger spontaneous firing of impaired neurons.
Moreover, the posterior insula is responsible for mental body schema representation and can produce tactile hallucination if defected.