Pancreatic cancer
[2] Pancreatic cancer is usually diagnosed by a combination of medical imaging techniques such as ultrasound or computed tomography, blood tests, and examination of tissue samples (biopsy).
[14] There are some studies that link high levels of red meat consumption to increased risk of pancreatic cancer, though meta-analyses typically find no clear evidence of a relationship.
[21] Neuroendocrine cancers have better outcomes; at five years from diagnosis, 65% of those diagnosed are living, though survival considerably varies depending on the type of tumor.
The small minority of cancers that arise in the hormone-producing (endocrine) tissue of the pancreas have different clinical characteristics and are called pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, sometimes abbreviated as "PanNETs".
The functioning types secrete hormones such as insulin, gastrin, and glucagon into the bloodstream, often in large quantities, giving rise to serious symptoms such as low blood sugar, but also favoring relatively early detection.
Cancer associated fibroblasts secrete fibrous tissue (desmoplasia) consisting of matrix metalloproteinases and hyaluronan which blocks the host's CD8+ T-cells from reaching the tumor.
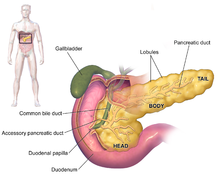
[3][12][34] The symptoms at diagnosis vary according to the location of the cancer in the pancreas, which anatomists divide (from left to right on most diagrams) into the thick head, the neck, and the tapering body, ending in the tail.
[34] A doctor may suspect pancreatic cancer when the onset of diabetes in someone over 50 years old is accompanied by typical symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, persistent abdominal or back pain, indigestion, vomiting, or fatty feces.
[57] Medical imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT scan) and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) are used both to confirm the diagnosis and to help decide whether the tumor can be surgically removed (its "resectability").
[34] Abdominal ultrasound is less sensitive and will miss small tumors, but can identify cancers that have spread to the liver and build-up of fluid in the peritoneal cavity (ascites).
[12] Liver function tests can show a combination of results indicative of bile duct obstruction (raised conjugated bilirubin, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase and alkaline phosphatase levels).
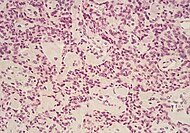
[54] The most common form of pancreatic cancer (adenocarcinoma) is typically characterized by moderately to poorly differentiated glandular structures on microscopic examination.
[3] Locally advanced adenocarcinomas have spread into neighboring organs, which may be any of the following (in roughly decreasing order of frequency): the duodenum, stomach, transverse colon, spleen, adrenal gland, or kidney.
Typical sites for metastatic spread (stage IV disease) are the liver, peritoneal cavity and lungs, all of which occur in 50% or more of fully advanced cases.
[69] A 2014 review of research concluded that there was evidence that consumption of citrus fruits and curcumin reduced risk of pancreatic cancer, while there was possibly a beneficial effect from whole grains, folate, selenium, and non-fried fish.
[88] A 2023 meta-analysis found clinical evidence that the FOLFIRINOX regimen provided better overall survival (OS) than gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel; both increased the risk of serious grade 3/4 adverse events.
The previously promoted gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel regimen offered insignificant OS or quality of life (QoL) improvement (66% risk of death at 12 months (RoD) versus control group's 63%).
[2] A 2025 study reports that a phase 1 clinical trial has found promising results for personalized mRNA vaccines as a potential treatment for pancreatic cancer.
Researchers then used genetic material from each patient’s tumor to create customized mRNA vaccines, designed to help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
Treatment may involve a variety of approaches, including draining the stomach by nasogastric aspiration and drugs called proton-pump inhibitors or H2 antagonists, which both reduce production of gastric acid.
[2] Outcomes are much better for PanNETs: Many are benign and completely without clinical symptoms, and even those cases not treatable with surgery have an average five-year survival rate of 16%,[65] although the outlook varies considerably according to the type.
[33] For locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinomas, which together represent over 80% of cases, numerous trials comparing chemotherapy regimes have shown increased survival times, but not to more than one year.
In the United States, the risk for African Americans is over 50% greater than for whites, but the rates in Africa and East Asia are much lower than those in North America or Europe.
[10] The annual incidence of clinically recognized pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs) is low (about 5 per one million person-years) and is dominated by the non-functioning types.
[24][31] Studies of autopsies have uncovered small PanNETs rather frequently, suggesting that the prevalence of tumors that remain inert and asymptomatic may be relatively high.
Some case reports were published in the 1820s and 1830s, and a genuine histopathologic diagnosis was eventually recorded by the American clinician Jacob Mendes Da Costa, who also doubted the reliability of Morgagni's interpretations.
Recognition of a non-insulin-secreting type of PanNET is generally ascribed to the American surgeons, R. M. Zollinger and E. H. Ellison, who gave their names to Zollinger–Ellison syndrome, after postulating the existence of a gastrin-secreting pancreatic tumor in a report of two cases of unusually severe peptic ulcers published in 1955.
Early operations were compromised partly because of mistaken beliefs that people would die if their duodenum were removed, and also, at first, if the flow of pancreatic juices stopped.
[131] The knowledge that new onset of diabetes can be an early sign of the disease could facilitate timely diagnosis and prevention if a workable screening strategy can be developed.
[134] Irreversible electroporation is a relatively novel ablation technique with potential for downstaging and prolonging survival in persons with locally advanced disease, especially for tumors in proximity to peri-pancreatic vessels without risk of vascular trauma.