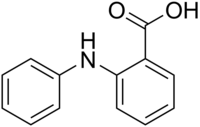
Fenamic acid
Fenamic acid is an organic compound, which, especially in its ester form, is called fenamate.
[1]: 458 serves as a parent structure for several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including mefenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, flufenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid.
These drugs are commonly referred to as "anthranilic acid derivatives" or "fenamates" because fenamic acid is a derivative of anthranilic acid.
[2]: 235 [3]: 17 [2] Fenamic acid can be synthesized from 2-chlorobenzoic acid and can be converted into acridone.
[4]