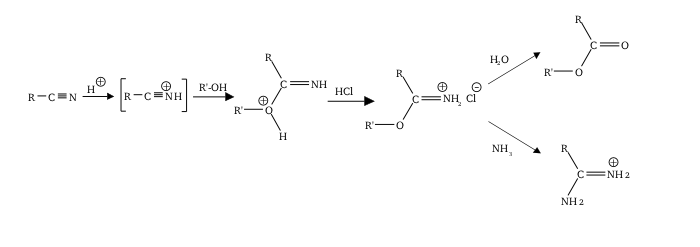
Pinner reaction
[2][3][4] Pinner salts are themselves reactive and undergo additional nucleophilic additions to give various useful products:[5][6] Commonly, the Pinner salt itself is not isolated, with the reaction being continued to give the desired functional group (orthoester etc.)
[8] It should be appreciated that the Pinner reaction refers specifically to an acid catalyzed process, but that similar results can often be achieved using base catalysis.
The two approaches can be complementary, with nitriles which are unreactive under acid conditions often giving better results in the presence of base, and vice versa.
For example: an electron-poor nitrile is a good electrophile (readily susceptible to attack from alkoxides etc.)
but a poor nucleophile would typically be easier to protonate than to participate in the reaction and hence would be expected to react more readily under basic rather than acidic conditions.