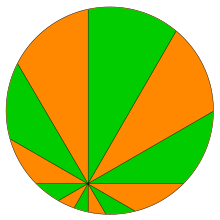
Pizza theorem
In elementary geometry, the pizza theorem states the equality of two areas that arise when one partitions a disk in a certain way.
The published solution to this problem, by Michael Goldberg, involved direct manipulation of the algebraic expressions for the areas of the sectors.
Cibulka et al. (2010) and Knauer, Micek & Ueckerdt (2011) study the game theory of choosing free slices of pizza in order to guarantee a large share, a problem posed by Dan Brown and Peter Winkler.
The two-dimensional version implies that any pizza, no matter how misshapen, can have its area and its crust length simultaneously bisected by a single carefully chosen straight-line cut.
The three-dimensional version implies the existence of a plane cut that equally shares base, tomato and cheese.