Proline organocatalysis
This theme is often considered the starting point for the area of organocatalysis, even though early discoveries went unappreciated.
[2]: 5574 [3] Proline catalysis was initially reported by groups at Schering AG and Hoffmann-La Roche.
[1][4][5][6] Proline's chiral structure enables enantioselective synthesis, favoring a particular enantiomer or diastereomer.
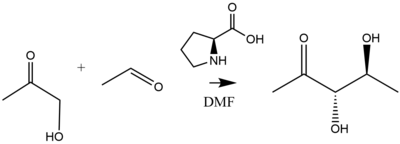
[34] Illustrating an enolexo intramolecular aldolization, dicarbonyl (dials,diketones) can be converted to anti-aldol products with a 10% L-proline catalyst loading.
[37] As refined by List and Notz, the aforementioned reaction produces diol products as follows:[38] Proline-catalyzed aldol additions proceed via a six-membered enamine transition state according to the Zimmerman-Traxler model.